Lid-driven cavity
Standard CFD benchmark, which allows comparison with very accurate mesh-based methods. Description of the problem can be found on many webpages, like here. In the image below, you can see streamlines for Re = 400 and N = 320. This was computed on cluster and took some time. To correctly resolve corner vortices is much more demanding in SPH than in FEM.
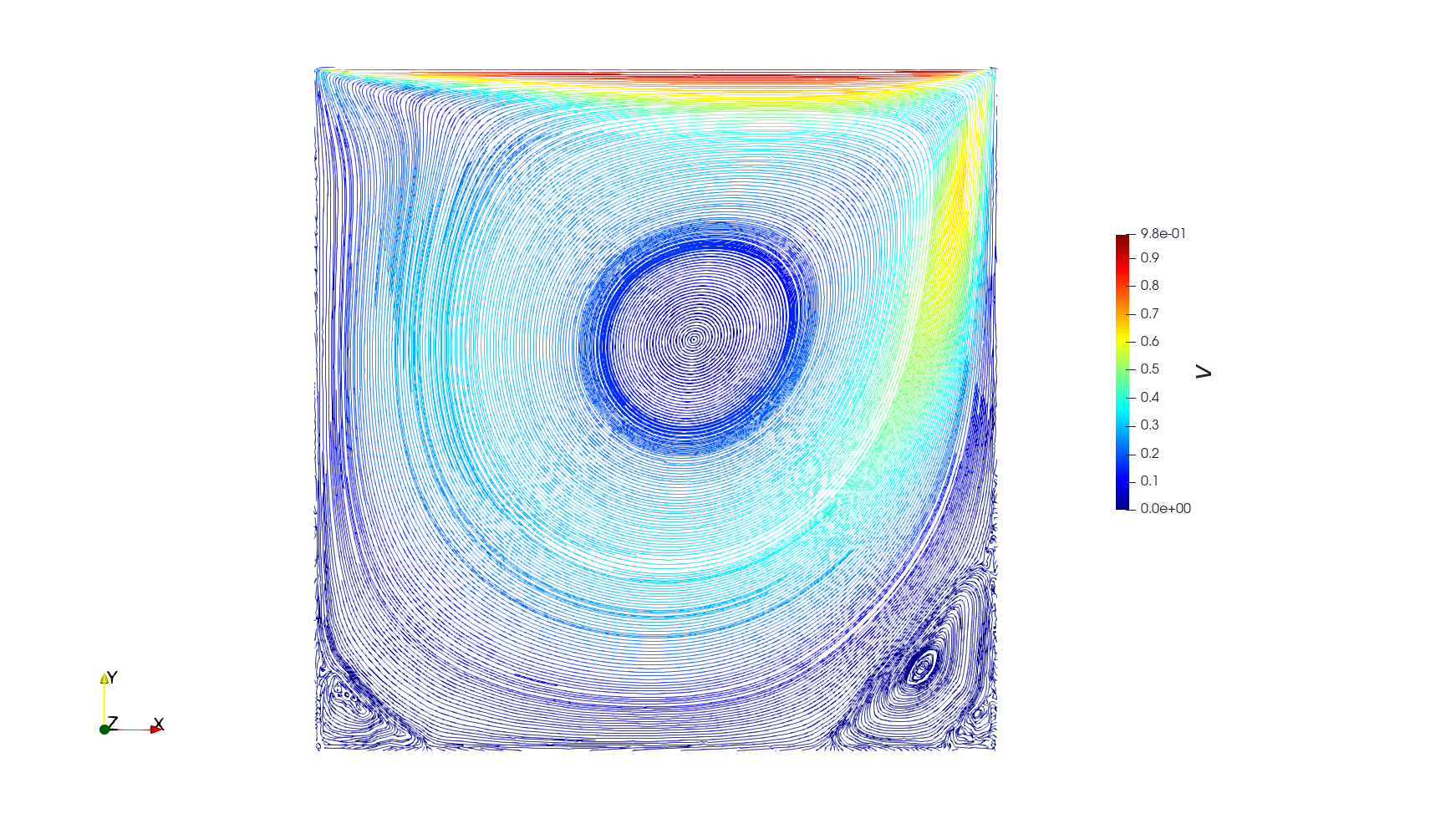
Result is compared to the referential solution by Ghia et al 1980.
module cavity_flow
using Printf
using SmoothedParticles
using Plots, CSV, DataFrames, Printf, LaTeXStrings, ParametersDeclare const parameters (dimensionless problem)
##geometrical/physical parameters
const N = 100 #number of sample points
const Re = 100 #Reynolds number
const llid = 1.0 #length of the lid
const mu = 1.0/Re #viscosity
const rho0 = 1.0 #density
const vlid = 1.0 #flow speed of the lid
const dr = llid/N #interparticle distance
const h = 3.0*dr #size of kernel support
const m = rho0*dr^2 #particle mass
const c = 20*vlid #numerical speed of sound
const P0 = 5.0 #background pressure (good to prevent tensile instability)
const wwall = h
##temporal parameters
const dt = 0.1*h/c #numerical time-step
const t_end = 0.4 #end of simulation
const dt_frame = max(dt, t_end/200) #how often save data
##particle types
const FLUID = 0.
const WALL = 1.
const LID = 2.
##path to store results
const path = "results/cavity_flow"*string(Re)Declare variables to be stored in a Particle
@with_kw mutable struct Particle <: AbstractParticle
x::RealVector=VEC0 #position
v::RealVector=VEC0 #velocity
Dv::RealVector=VEC0 #acceleratation
rho::Float64=rho0 #density
Drho::Float64=0.0 #rate of density
P::Float64=0.0 #pressure
type::Float64 #particle type
endDefine geometry and create particles
function make_system()
grid = Grid(dr, :hexagonal)
box = Rectangle(0., 0., llid, llid)
wall = BoundaryLayer(box, grid, wwall)
sys = ParticleSystem(Particle, box + wall, h)
lid = Specification(wall, x -> x[2] > llid)
wall = Specification(wall, x -> x[2] <= llid)
generate_particles!(sys, grid, box, x -> Particle(x=x, type=FLUID))
generate_particles!(sys, grid, lid, x -> Particle(x=x, type=LID))
generate_particles!(sys, grid, wall, x -> Particle(x=x, type=WALL))
create_cell_list!(sys)
apply!(sys, find_pressure!)
apply!(sys, internal_force!)
return sys
endDefine interactions between particles
function balance_of_mass!(p::Particle, q::Particle, r::Float64)
p.Drho += m*rDwendland2(h,r)*(dot(p.x-q.x, p.v-q.v))
end
function find_pressure!(p::Particle)
p.rho += p.Drho*dt
p.Drho = 0.0
p.P = P0 + c^2*(p.rho-rho0)
end
function internal_force!(p::Particle, q::Particle, r::Float64)
rDk = rDwendland2(h,r)
x_pq = p.x - q.x
v_pq = p.v - q.vimplementation of the Dirichlet boundary condition at the lid v_q is estimated using linear extrapolation
if q.type == LID
s = abs(x_pq[2])/(0.1*h + abs(p.x[2] - 1.0))
v_pq = s*(p.v - vlid*VECX)
end
p.Dv += -m*rDk*(p.P/p.rho^2 + q.P/q.rho^2)*x_pq
p.Dv += 8/(Re*p.rho*q.rho)*m*rDk*dot(v_pq, x_pq)/(r^2 + 0.01*h^2)*x_pq #Monaghan's type of viscosity to conserve angular momentum
end
function move!(p::Particle)
p.Dv = VEC0
if p.type == FLUID
p.x += 0.5*dt*p.v
end
end
function accelerate!(p::Particle)
if p.type == FLUID
p.v += 0.5*dt*p.Dv
end
endTime iteration
function main()
sys = make_system()
out = new_pvd_file(path)
@time for k = 0 : Int64(round(t_end/dt))
apply!(sys, accelerate!)
apply!(sys, move!)
create_cell_list!(sys)
apply!(sys, balance_of_mass!)
apply!(sys, find_pressure!)
apply!(sys, move!)
create_cell_list!(sys)
apply!(sys, internal_force!)
if (k % Int64(round(dt_frame/dt)) == 0) #save the frame
@printf("t = %.6e s ", k*dt)
println("(",round(100*k*dt/t_end),"% complete)")
save_frame!(out, sys, :P, :v, :type)
end
apply!(sys, accelerate!)
end
save_pvd_file(out)
compute_fluxes(sys)
make_plot()
endFunctions to extract results and create plots.
function compute_fluxes(sys::ParticleSystem, res = 100)
s = range(0.,1.,length=res)
v1 = zeros(res)
v2 = zeros(res)
for i in 1:res
#x-velocity along y-centerline
x = RealVector(0.5, s[i], 0.)
gamma = SmoothedParticles.sum(sys, (p,r) -> Float64(p.type==FLUID)*m*wendland2(h,r), x)
v1[i] = SmoothedParticles.sum(sys, (p,r) -> Float64(p.type==FLUID)*m*p.v[1]*wendland2(h,r), x)/gamma
#y-velocity along x-centerline
x = RealVector(s[i], 0.5, 0.)
gamma = SmoothedParticles.sum(sys, (p,r) -> Float64(p.type==FLUID)*m*wendland2(h,r), x)
v2[i] = SmoothedParticles.sum(sys, (p,r) -> Float64(p.type==FLUID)*m*p.v[2]*wendland2(h,r), x)/gamma
end
#save results into csv
data = DataFrame(s=s, v1=v1, v2=v2)
CSV.write(path*"/data.csv", data)
make_plot()
end
function make_plot(Re=Re)
ref_x2vy = CSV.read("reference/ldc-x2vy.csv", DataFrame)
ref_y2vx = CSV.read("reference/ldc-y2vx.csv", DataFrame)
propertyname = Symbol("Re", Re)
ref_vy = getproperty(ref_x2vy, propertyname)
ref_vx = getproperty(ref_y2vx, propertyname)
ref_x = ref_x2vy.x
ref_y = ref_y2vx.y
data = CSV.read(path*"/data.csv", DataFrame)
p1 = plot(
data.s, data.v2,
xlabel = L"x",
ylabel = L"v_y",
label = "SPH",
linewidth = 4,
legend = :bottomleft,
color = :orange,
tickfontsize = 16,
labelfontsize = 16,
legendfontsize = 16,
aspect_ratio = 1,
)
scatter!(p1, ref_x, ref_vy, label = "REF", markershape = :diamond, ms = 5, color = :blue)
savefig(p1, path*"/ldc-x2vy.pdf")
p2 = plot(
data.v1, data.s,
xlabel = L"v_x",
ylabel = L"y",
label = "SPH",
linewidth = 4,
legend = :bottomright,
color = :orange,
tickfontsize = 16,
labelfontsize = 16,
legendfontsize = 16,
aspect_ratio = 1,
)
scatter!(p2, ref_vx, ref_y, label = "REF", markershape = :diamond, ms = 5, color = :blue)
savefig(p2, path*"/ldc-y2vx.pdf")
end
endThis page was generated using Literate.jl.