Water collapse (explicit)
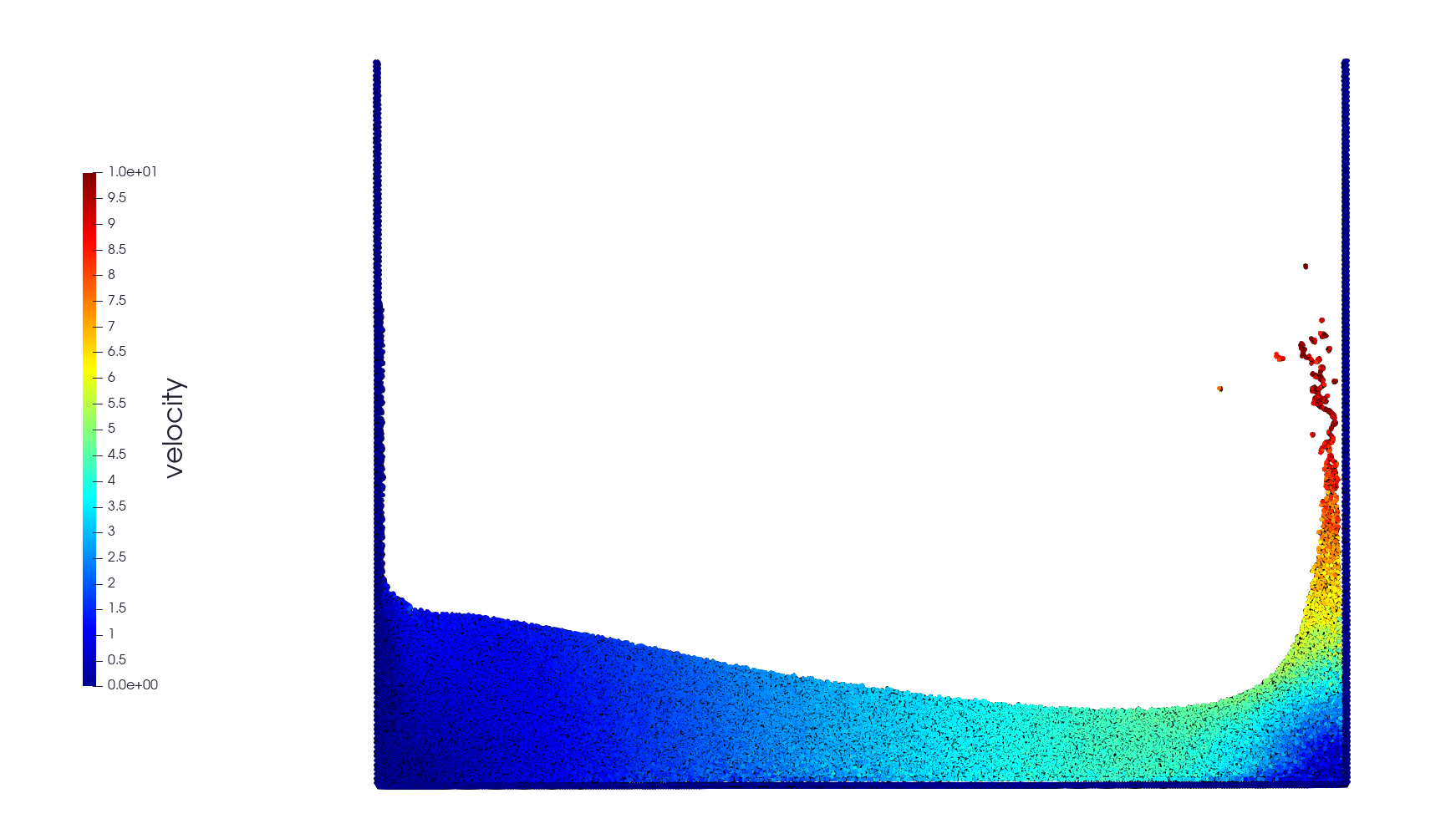
Simulation of a water column collapsing under its own weight. This would be very difficult to make in a mesh-based method like FDM, FEM or FVM. Fortunately, SPH turns this into an easy task. We use a very basic explicit SPH scheme with pressure-stabilized Verlet time integrator. This benchmark is (more or less) a recomputation of a simulation described in D. Violeau, FLUID MECHANICS AND THE SPH METHOD, page 484. We show how to implement it using SmoothedParticles.jl. Dependencies can be installed with
import Pkg
Pkg.add("Printf")
Pkg.add("CSV")
Pkg.add("DataFrames")
Pkg.add("Parameters")
Pkg.add("Plots")Import essential packages.
module collapse_dry
using Printf
using SmoothedParticles
using CSV
using DataFrames
using Parameters
using PlotsConstant parameters
Importantly, modifier const avoids memory allocations.
# physical
const dr = 1.5e-2 # average particle distance (decrease to refine, increase to speed up)
const h = 3.0*dr # size of kernel radius (twice the smoothing length)
const rho0 = 1000. # fluid density
const m = rho0*dr^2 # particle mass
const c = 50.0 # numerical speed of sound
const g = -7.0*VECY # gravitational acceleration
const mu = 8.4e-4 # dynamic viscosity of water
const nu = 1.0e-6 # artificial pressure stabilization
# geometrical
const water_column_width = 1.0
const water_column_height = 2.0
const box_height = 3.0
const box_width = 4.0
const wall_width = 2.5*dr
# temporal
const dt = 0.1*h/c # numerical time step
const t_end = 4.0 # when to terminate (in seconds)
const dt_frame = max(dt,t_end/200) # time step in the output (dt = dt_frame would save every frame, generating huge files)
##particle types
const FLUID = 0. # fluid marker
const WALL = 1. # wall markerParticle variables
@with_kw mutable struct Particle <: AbstractParticle
x::RealVector # position
v::RealVector = VEC0 # velocity
Dv::RealVector = VEC0 # acceleration
rho::Float64 = rho0 # density
Drho::Float64 = 0. # rate of density
P::Float64 = 0. # pressure
type::Float64 # particle_type
endGeometry
function make_system()
grid = Grid(dr, :hexagonal) # use hexagonal grid
box = Rectangle(0., 0., box_width, box_height) # laboratory box
fluid = Rectangle(0., 0., water_column_width, water_column_height) # column of fluid
walls = BoundaryLayer(box, grid, wall_width) # walls around laboratory box
walls = Specification(walls, x -> (x[2] < box_height)) # remove top lid
sys = ParticleSystem(Particle, box + walls, h) # define particle system by specifying particle type, domain and maximal kernel radius
generate_particles!(sys, grid, fluid, x -> Particle(x=x, type=FLUID)) # fill fluid geometry with particles
generate_particles!(sys, grid, walls, x -> Particle(x=x, type=WALL)) # fill wall geometry with particles
for p in sys.particles
p.P = rho0*g[2]*(p.x[2] - water_column_height) # hydrostatic pressure
p.rho = rho0 + p.P/c^2 # solve for density
end
return sys
endParticle interactions
Rate of density is
$\dot{\varrho}_p = \sum_q m_q \left( \mathbf{x}_{pq} \cdot \mathbf{v}_{pq} + 2 \nu \varrho_{pq} \right) \frac{w'_{pq}}{r_{pq}}$
function balance_of_mass!(p::Particle, q::Particle, r::Float64)
ker = m*rDwendland2(h,r)
p.Drho += ker*(dot(p.x-q.x, p.v-q.v) + 2*nu*(p.rho-q.rho))
endLinear formula for pressure. Tait equation can be used instead but the difference is mostly negligible.
$P_p = c^2 (\varrho_p - \varrho_0)$
function find_pressure!(p::Particle)
p.rho += p.Drho*dt
p.Drho = 0.0
p.P = c^2*(p.rho - rho0)
endInternal forces between particles are pressure and viscosity. Wall particles are excluded.
$\dot{\mathbf{v}}_p = -\sum_q m_q \left( \frac{P_p}{\rho_p^2} + \frac{P_q}{\rho_q^2} \right) \frac{w'_{pq}}{r_{pq}} \mathbf{x}_{pq} + \frac{2 \mu}{\rho_0^2}\sum_q m_q \frac{w'_{pq}}{r_{pq}} \mathbf{v}_{pq}$
function internal_force!(p::Particle, q::Particle, r::Float64)
if p.type == FLUID
ker = m*rDwendland2(h,r)
p.Dv += -ker*(p.P/p.rho^2 + q.P/q.rho^2)*(p.x - q.x)
p.Dv += +2*ker*mu/rho0^2*(p.v - q.v)
end
endPosition and velocity updates
Updating by half-time step is a feature of Verlet integrator.
function move!(p::Particle)
p.Dv = VEC0
if p.type == FLUID
p.x += 0.5*dt*p.v
end
end
function accelerate!(p::Particle)
if p.type == FLUID
p.v += 0.5*dt*(p.Dv + g)
end
endExtract global variables
Variables of interest are total energy, water column height and wavefront location.
function energy(p::Particle)::Float64
kinetic = 0.5*m*dot(p.v, p.v)
potential = -m*dot(g, p.x)
internal = m*c^2*(log(abs(p.rho/rho0)) + rho0/p.rho - 1.0)
return kinetic + potential + internal
end
function get_globals(sys::ParticleSystem)::NTuple{3,Float64}
H = 0.0 # height of water column
X = 0.0 # wavefront x-coordinate
E = 0.0 # total energy
for p in sys.particles
if p.type == FLUID
X = max(X, p.x[1]/water_column_width)
end
if p.type == FLUID && 2.0 > p.x[1] > h
H = max(H, p.x[2]/water_column_height)
end
E += energy(p)
end
return (X,H,E)
endTime loop
SmoothedParticles.jl will automatically run this in parallel and use neighbor list acceleration. Command create_cell_list!(sys) must be called at the beginning and each time after particles move.
function main()
ts = []
Xs = []
Hs = []
sys = make_system()
out = new_pvd_file("results/collapse_dry")
create_cell_list!(sys)
apply!(sys, internal_force!)
@time for k = 0 : round(Int64, t_end/dt)
apply!(sys, accelerate!)
apply!(sys, move!)
create_cell_list!(sys)
apply!(sys, balance_of_mass!)
apply!(sys, find_pressure!)
apply!(sys, move!)
create_cell_list!(sys)
apply!(sys, internal_force!)
apply!(sys, accelerate!)
# save data at selected frames
if (k % round(Int64, dt_frame/dt) == 0)
@printf("t = %.6e s ", k*dt)
println("(",round(100*k*dt/t_end),"% complete)")
(X, H, E) = get_globals(sys)
@printf("energy = %.6e J\n", E)
@printf("\n")
push!(Xs, X)
push!(Hs, H)
push!(ts, k*dt*sqrt(-2*g[2]))
save_frame!(out, sys, :v, :P, :type)
end
end
save_pvd_file(out)
data = DataFrame(time = ts, X = Xs, H = Hs)
CSV.write("results/collapse_dry/data.csv", data)
@info "drawing a plot with results"
make_plot()
end ## function mainCompare computed results to the book by Violeau and the experiment of Koshizuka and Oka (1996)
function make_plot()
data = CSV.read("results/collapse_dry/data.csv", DataFrame)
X_VIO = CSV.read("reference/dambreak_X_Violeau.csv", DataFrame)
X_KOS = CSV.read("reference/dambreak_X_Koshizuka.csv", DataFrame)
H_VIO = CSV.read("reference/dambreak_H_Violeau.csv", DataFrame)
H_KOS = CSV.read("reference/dambreak_H_Koshizuka.csv", DataFrame)
p1 = plot(data.time, data.X, label = "SmoothedParticles.jl", xlims = (0., 3.0))
scatter!(p1, X_VIO.time, X_VIO.X, label = "Violeau")
scatter!(p1, X_KOS.time, X_KOS.X, label = "Koshizuka&Oda", markershape = :square)
savefig(p1, "results/collapse_dry/dambreak_X.pdf")
p2 = plot(data.time, data.H, label = "SmoothedParticles.jl", xlims = (0., 3.0))
scatter!(p2, H_VIO.time, H_VIO.H, label = "Violeau")
scatter!(p2, H_KOS.time, H_KOS.H, label = "Koshizuka&Oda", markershape = :square)
savefig(p2, "results/collapse_dry/dambreak_H.pdf")
end
end ## moduleThis page was generated using Literate.jl.